We can’t send you updates from Justia Onward without your email.
Unsubscribe at any time.
Our annual round-up of developments in the online world discusses developments in internet marketing over the past year and looks forward to 2020.
2019 has come to a close, and as we’ve done the last few years, we wanted to take this opportunity to summarize how the landscape of the web has changed in the last year and take a look forward at things that are expected in 2020.
Accessibility Is Very Important
Making sure that your website is accessible to everyone has always been important for making sure that you don’t lose potential clients. However, recent developments in the federal courts may hold website owners liable in lawsuits if their sites are not ADA compliant.
In 2016, a blind individual named Guillermo Robles filed suit against Dominos Pizza in the Central District of California, alleging that the Dominos website was not accessible to blind users and that this violated the Americans with Disabilities Act. When the District Court dismissed the action, Robles appealed to the US Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit. The Ninth Circuit reversed that dismissal in January 2019, holding that the ADA applies to websites and apps. Dominos attempted to appeal this decision to the US Supreme Court, but the Supreme Court turned down the appeal in October, allowing the circuit court’s decision to stand.
By declining to hear the case, the Supreme Court has cleared the way for more lawsuits against companies without ADA-compliant websites.
Watch this video to learn how to make your law firm website accessible and ADA-compliant.
AMP Became More Powerful
The AMP Project continues to grow more powerful this year, with big releases like amp-script, which allows custom javascript. Building on that base, AMP can now be used in React-based sites through integration with Next.js. AMP for Email is now generally available, and dynamic emails powered by AMP can now be sent to GMail users, with Outlook and Yahoo support coming soon.
 There have also been major changes in the way in which the AMP community is organized. Shortly after their new governance model went into effect, reducing the ownership that Google had over AMP, the AMP Project announced that they were joining the OpenJS Foundation.
There have also been major changes in the way in which the AMP community is organized. Shortly after their new governance model went into effect, reducing the ownership that Google had over AMP, the AMP Project announced that they were joining the OpenJS Foundation.
Watch this clip to learn more about Accelerated Mobile Pages.
Online Privacy Is More Important Than Ever
Continuing the trend from 2018, Online Privacy has been continually in the news during 2019. In mid-2018, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) went into effect, and it caused a major change to the way that the web appears for everyone. Sites everywhere started putting up notices about their privacy policies and use of cookies on every page load in order to stay in compliance with GDPR. GDPR was only the beginning, however. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) will go into effect on January 1, 2020 and brings many of the same sorts of privacy protections that GDPR brought to Europe to citizens of the state of California.
Meanwhile, major tech companies have continually seen themselves under fire for breaches of privacy. The FTC fined Facebook $5 billion in July and demanded that Facebook adopt stricter privacy protection measures for users. The European Union fined Google $57 million for violating GDPR in January, and then it threatened even more hefty fines in May.
The FTC fined Google $170 million for violations of the much older COPPA law on YouTube, and as a result, Google has instituted new policies for YouTube content creators, requiring them to indicate if their content might possibly be interesting to children or not. If so, the amount of revenue that content creators can make on their videos will be severely limited by the lack of targeted advertising on their videos.
It is clear that the world is taking online privacy far more seriously than ever before. This trend really came into focus this year, and it will continue to affect the online landscape in 2020 and beyond.
The Algorithm Marches Forward
Google became a lot more transparent about their core algorithm updates this year. They started naming their algorithm updates themselves instead of letting SEO news sites name them. Starting in June, Google actually started giving developers advance notice of larger algorithm updates, rather than letting them discover the updates through changes in traffic patterns. They gave a similar update for September’s release.
Tomorrow, we are releasing a broad core algorithm update, as we do several times per year. It is called the June 2019 Core Update. Our guidance about such updates remains as we’ve covered before. Please see this tweet for more about that:https://t.co/tmfQkhdjPL
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) June 2, 2019
SearchEngineLand has a great round-up of all of Google’s algorithm changes for the year, if you are interested in reading more about all of the ways in which the algorithm changed this year.
Search Engine Result Pages Got a Facelift
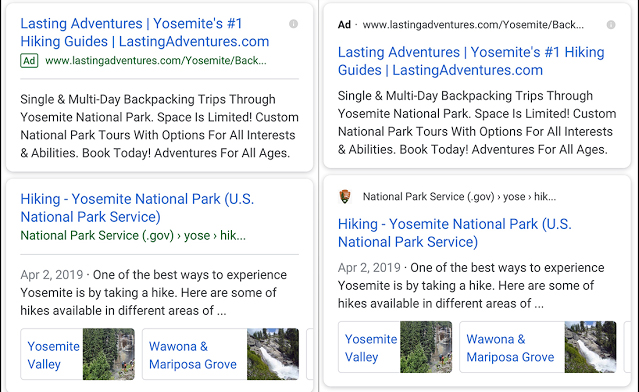 Earlier this year, Google rolled out a whole new look for search result pages on mobile. The new search result pages allow site owners to brand search results with the site name and icon above the page title.
Earlier this year, Google rolled out a whole new look for search result pages on mobile. The new search result pages allow site owners to brand search results with the site name and icon above the page title.
While it hasn’t been rolled out for desktop yet, multiple sources reported seeing the favicons in desktop search back in August. Google has long been fond of using A/B testing for user interface changes, in which they show a new user interface to a small percentage of users and gather statistics on how those users act compared to users viewing other user interfaces. While these reports died down in the fall, that doesn’t necessarily mean that Google isn’t planning on rolling out the revised look for desktop search in the future. It can often take time for Google’s teams to analyze all the data and then revise the final layout before release.
Results Without Clicks
According to a study of user data, June marked a milestone when over 50% of Google searches ended with no clicks to non-Google sites. While not necessarily the sole cause, it is not hard to draw a correlation to other studies that show that the occurrence of Rich Answers and Featured Snippets in Google Search results has increased dramatically in 2019 from previous years. Google has long been working toward directly answering users’ questions by using data from the Knowledge Graph built on Structured Data.
At Google I/O this year, Google announced new rich snippet support for FAQ and How-to type content. The new How-to markup can take information from your website and give users step-by-step instructions to do something, while the FAQ snippets can directly answer a user’s question with an answer from your website.
It is easy to understand why Google is pushing for more and more direct answers. The faster that users can get the information that they want, the happier they will be, and having direct answers to user questions can help when the users are asking their questions to a smart assistant, such as the Google Assistant, as well.
Predictably, reactions from web developers to this shift have been mixed. Website owners naturally want users to end up on their own websites, and with the rise of zero-click results, they can potentially get less traffic. However, it is worth pointing out that if you optimize for these new snippets, users can get answers to their questions from you (branded with your firm name) faster and with higher visibility, which can help with brand awareness and with reaching more users.
Google Improved Their Crawling in Several Ways
Google announced back in May that the Mobile-First index would be the default crawling of all newly discovered websites as of July 1. Many existing websites have already been converted to mobile-first indexing, and Google continues to update their crawling of existing sites. Eventually, all sites will be indexed by the mobile version of Googlebot.

Evergreen Googlebot Announcement Slide at Google I/O 2019
Also announced in May at the Google I/O Developer conference, Google’s crawler, Googlebot, is now “evergreen.” Prior to this, Googlebot has been based on a fairly old version of Chrome (Chrome 41, which was released back in 2015), and this resulted in newer web technologies being ignored by the Google crawler. Starting in May, Google committed to continually update Googlebot to new versions of Chrome from now on, making sure that what Googlebot sees when it indexes your site is the same thing that users of up-to-date web browsers see.
In an effort to improve handling of robots.txt directives, Google announced in July that they were working with the original creator of the robots.txt protocol to finally standardize the protocol by submitting a working draft to the IETF. At the same time, they open sourced Googlebot’s robots.txt parser in an effort to make it easier for other entities to adopt the new IETF draft protocol.
The concept of the nofollow link was expanded in September with new rel="sponsored" and rel="ugc" attributes for links in addition to the existing less-specific rel="nofollow" attribute. These new attributes allow developers to indicate in which way the links are different from other links on the page.
Google has also spent time this year clarifying misconceptions that many developers have had for a long time. In March, John Mueller indicated that Google hadn’t supported rel="next" or rel="prev" for determining pagination for several years and just hadn’t told anyone. In October, Mueller clarified that in spite of what many SEO experts have been spouting for years, Google’s systems don’t get confused if there is more than one H1 tag on a page. It is worth noting that in spite of these revelations, both rel=next/prev and structuring your heading tags on a page are considered good practices for accessibility.
Into the Next Decade
As we enter 2020, it is clear that the web as a whole is in a state of flux, with online privacy laws around the globe evolving constantly and ADA compliance becoming a requirement. It has never been more important to follow best practices in your online marketing efforts to protect your interests. With the overwhelming majority of web search traffic taking place on mobile devices, high-performance and mobile-optimized sites are absolutely crucial for success. With search engines valuing data more than text, keeping on top of the constantly changing landscape of Structured Data Markup is vital.
If you are looking to update your law firm’s web presence to a new mobile-friendly, AMP-compatible, ADA-compliant website that is highly optimized with Structured Data to get your content into the rich snippets and verbal assistant responses that are increasingly dominating search results, contact us. Our team of experts has tons of experience with all things web-related, and we are constantly staying on top of the latest developments in online marketing. We’ll make sure that your site is ready for all these developments and stays up to date with changes in online marketing as they happen.